Prototyping serves as a cornerstone for transforming abstract ideas into tangible user experiences. From conceptualization to final execution, prototyping plays a pivotal role in validating design decisions, gathering feedback, and refining interfaces for optimal usability and engagement. This comprehensive guide elaborates the significance of prototyping in UI/UX design, exploring its various stages, methodologies, and best practices.
Understanding Prototyping in UI/UX Design
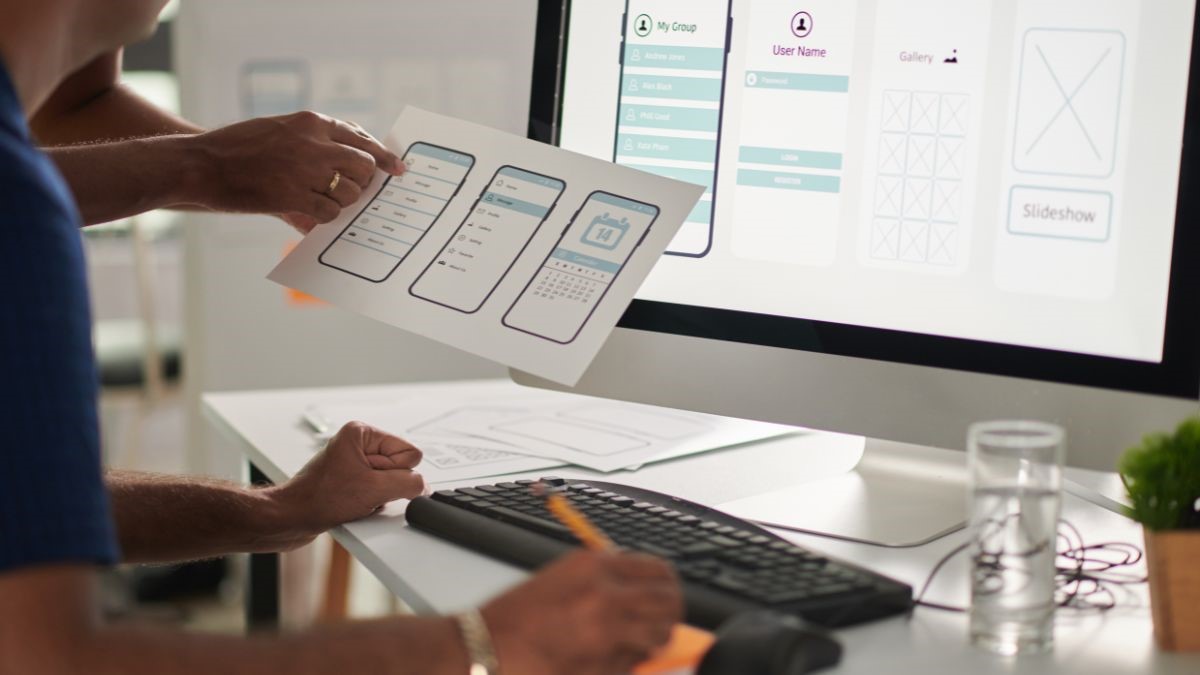
Prototyping involves the creation of interactive mockups or wireframes that simulate the functionality and flow of a digital product or application. Unlike static design mockups, prototypes enable designers to test user interactions, navigation paths, and interface elements in a dynamic environment. By presenting stakeholders with a tangible representation of the final product, prototypes facilitate collaboration, iteration, and refinement throughout the design process.
Stages of Prototyping
Prototyping in UI/UX design typically follows a phased approach, encompassing several stages from initial ideation to final validation:
1. Conceptualization: In the conceptualization phase, designers brainstorm ideas, define user requirements, and establish design goals and objectives. Prototyping at this stage involves creating low-fidelity wireframes or sketches to explore different layout options and user flows.
2. Iterative Design: During the iterative design phase, designers refine and iterate on initial concepts based on user feedback and usability testing. Prototypes evolve from low-fidelity to high-fidelity representations, incorporating more detailed design elements and interactive components.
3. Validation and Testing: The validation and testing phase involves gathering feedback from users through user friendly accessibility and usability testing. Prototypes serve as testable hypotheses, allowing designers to assess user interactions, identify pain points, and validate design assumptions before final implementation.
4. Refinement and Finalization: Based on feedback and insights gathered during testing, designers refine and finalize the prototype. They make necessary adjustments to improve usability, accessibility, and overall user experience. Prototyping tools facilitate rapid iteration and collaboration, streamlining the design refinement process.
Prototyping Methodologies and Best Practices
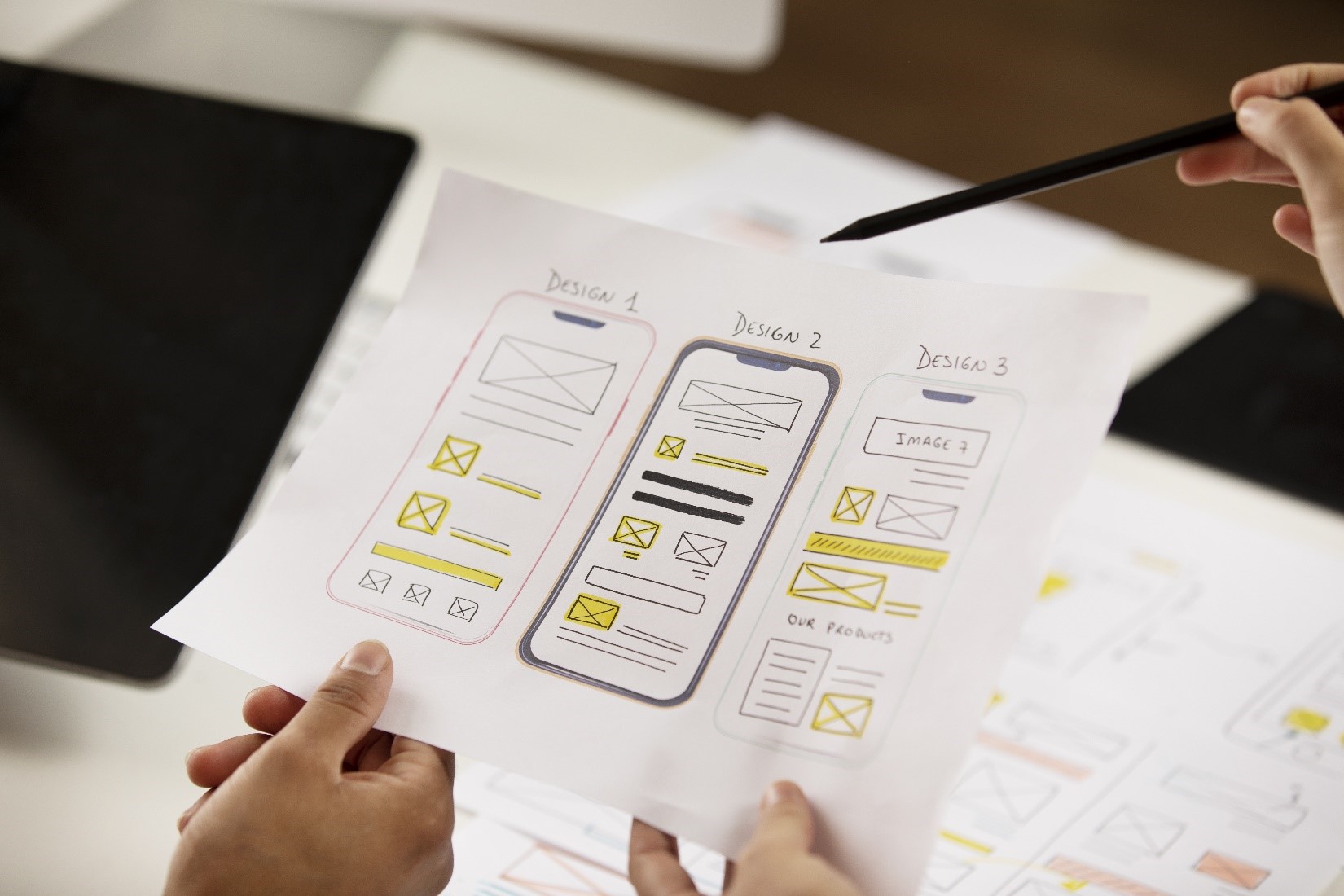

Several prototyping methodologies and best practices guide designers in creating effective prototypes that align with user needs and project requirements:
1. Low-Fidelity vs. High-Fidelity Prototypes: Low-fidelity prototypes focus on basic layout and functionality, while high-fidelity prototypes include detailed design elements and interactive features. Designers choose the appropriate fidelity level based on project scope, timeline, and testing objectives.
2. Interactive Prototyping Tools: A wide range of prototyping tools, such as Sketch, Adobe XD, Figma, and InVision, offer features for creating interactive prototypes with clickable links, animations, and transitions. These tools empower designers to simulate user interactions and test interface functionality in a realistic manner.
3. User-Centered Design Principles: Prototyping should adhere to user-centered design principles, prioritizing user needs, preferences, and behaviors. Designers conduct user research, create user personas, and employ usability heuristics to inform prototyping decisions and ensure an intuitive and user-friendly interface.
4. Collaborative Prototyping: Collaboration is essential in prototyping, involving cross-functional teams, stakeholders, and end-users throughout the design process. Collaborative prototyping platforms enable real-time feedback, version control, and remote collaboration, fostering a shared understanding of design goals and objectives.
Benefits of Prototyping in UI/UX Design
_1715680163.jpeg)
Prototyping offers numerous benefits for UI/UX design projects, including:
1. Early Validation: Prototypes enable early validation of design concepts and user interactions, reducing the risk of costly redesigns and development errors later in the project lifecycle.
2. Iterative Improvement: Through rapid iteration and testing, prototypes facilitate continuous improvement and refinement of the user experience, leading to more effective and user-centric designs.
3. Stakeholder Alignment: Prototypes serve as visual communication tools, aligning stakeholders and project teams around a shared vision for the final product and fostering support throughout the design process.
4. Risk Mitigation: By identifying usability issues early in the process, prototypes help mitigate project risks and ensure a seamless transition from design to development.
Enhancing UI/UX Design Through User Research and Personas at CSM Tech
At CSM Tech, we recognize the importance of user research and personas in UI/UX design. Our UI/UX services are designed to dive deep into user preferences and behaviors, guiding design decisions with data-driven insights.
We understand the significance of prototyping in UI/UX design and offer comprehensive services to support your business needs. From low-fidelity wireframes to high-fidelity interactive mockups, we work closely with you to bring your vision to life and create impactful user experiences. Let us partner with you on your next UI/UX design project, and together, we can build products that drive value and success for business.
Ready to elevate your UI/UX design? Contact us today to learn more and get started
Want to start a project?
Get your Free ConsultationOur Recent Blog Posts

© 2025 CSM Tech Americas All Rights Reserved